The Potential Impact of New Trade Tariffs and Market Volatility on Digital Health
Introduction: Mounting Tariff Pressures and Market Volatility
Despite rising trade tensions and economic volatility, Q1 2025 saw unexpected resilience in Digital Health deal-making. M&A activity rose 21% year-over-year, with 80% of acquisitions occurring in the United States, reflecting a trend toward domestic consolidation. Simultaneously, global equity funding totalled $6.3 billion, up 2% YoY, driven by a remarkable 82% surge in European investments, suggesting growing regional diversification in capital flows.
However, this resilience might soon be tested. In April 2025, the U.S. administration imposed a universal 10% tariff on imports, with significantly higher rates on select countries, notably a 125% tariff on Chinese goods. The administration also signalled potential semiconductor tariffs, which could profoundly impact sectors like Digital Health that rely heavily on advanced chips. Adding further pressure, concerns over a possible U.S. dollar devaluation are mounting, which could increase the costs of imported healthcare technologies.
In response, global trade partners—including China and Europe—are reportedly preparing or implementing counter-tariffs on U.S. goods, escalating the risk of a prolonged trade war. These retaliatory measures might compound the financial strain on healthcare technology companies, increasing operating costs and disrupting global supply chains.
For Digital Health stakeholders, these developments might present significant risks: rising hardware costs, constrained capital availability, hesitant corporate partners, and market volatility. The following explores how these dynamics could reshape the Digital Health ecosystem in the months ahead.
Rising Hardware and Device Costs
The cost of Digital Health devices and hardware—including wearables, sensors, and diagnostics equipment—might rise sharply due to the combined effects of import tariffs, a potential U.S. dollar devaluation, and semiconductor tariffs. These pressures could erode tight margins for startups and scale-ups that rely on globally sourced components and lean manufacturing.
A significant portion of the sector’s innovation depends on access to affordable hardware, and any spike in costs might be passed on to healthcare providers and patients, reducing adoption rates and slowing innovation cycles.
If semiconductor tariffs materialise, they could dramatically impact the cost structures of Digital Health ventures, as chips form the backbone of everything from remote monitoring devices to AI-powered diagnostics.
Innovation Bottlenecks and Global Collaboration Risks
The Digital Health ecosystem thrives on global collaboration through cross-border research partnerships, outsourced development, or international supply chains. However, tariff-driven cost increases and geopolitical tensions could create friction in these relationships, particularly affecting smaller companies that might lack the scale to absorb price shocks.
Innovation pipelines could narrow, as companies might delay or scale back R&D investments, slowing the rollout of next-generation healthcare technologies.
IPO Market: A Window Narrowing Further
The digital health IPO market might continue to struggle as market volatility dampens investor confidence. In 2025 YTD, only one IPO—Beta Bionics, a U.S.-based company—has been disclosed, compared to three IPOS during the same period in 2024.
As valuations fluctuate and market sentiment weakens, more companies might delay their public offerings, leading to a bottleneck in exit opportunities for growth-stage investors. This could further reduce the capital available for scaling Digital Health ventures, slowing momentum across the sector.
Corporate Decision-Making: From Bold to Cautious
Corporations already grappling with digital transformation might face rising operating costs due to tariffs on imported components. Many could be forced into cost restructuring programs to accommodate these higher costs, limiting the capital available for new initiatives such as Digital Health pilots and partnerships.
This shift toward operational caution might delay strategic investments in emerging healthcare technologies. Indeed, the Financial Times reported that “recession” was mentioned in 44% of Q1 2025 earnings calls, up dramatically from 3% in Q4 2024. This heightened recession anxiety might reinforce a short-term focus among corporates, steering them away from transformational projects toward immediate cost containment.
Reflecting this cautious stance, the number of disclosed Digital Health partnerships in Q1 2025 stood at 640, representing a 34% year-over-year decline. This drop suggests that corporates might pull back from collaborative innovation, prioritising core operations over broader ecosystem engagement.
Investor Sentiment: Defensive and Increasingly Domestic
Investor sentiment toward Digital Health might remain increasingly defensive as market volatility and trade policy uncertainty persist. Many venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) investors could become even more domestic in deploying their funds, focusing on U.S.-based assets perceived as safer amid global turbulence.
This homeward shift in investment strategy could exacerbate regional fragmentation within the Digital Health ecosystem, slowing cross-border capital flows and stifling international collaboration.
The data reflects this cooling sentiment: in April 2024, $3.5 billion was invested in Digital Health globally. As of 23 April 2025, only $1.4 billion had been invested—a stark decline that underscores the risk aversion gripping investors. VC and PE dealmaking might continue to slow, with firms adopting more structured terms, including liquidation preferences and earnouts, and extending due diligence cycles.
Digital Health founders might also continue to face higher standards for raising capital, often needing to prove commercial viability earlier than their Biotech or MedDev counterparts.
Consolidation as a Survival Strategy
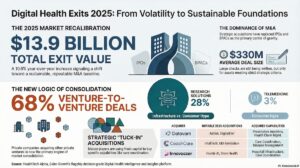
Given these financial pressures, Digital Health consolidation could accelerate as companies seek mergers or acquisitions to pool resources and achieve scale. In 2024, 70% of all M&A activity in the sector was venture-to-venture, driven by the need to reduce costs and expand offerings.
Regional consolidation might intensify, with Europe and other markets fostering local Digital Health champions. This could lessen reliance on U.S. capital and platforms, reshaping the global innovation landscape.
Conclusion: A Sector at a Crossroads
The Digital Health sector might be heading into a period of intensified pressure, marked by rising costs, constrained capital, corporate caution, and IPO market weakness. While these headwinds could stall momentum, they also present opportunities for resilient companies and forward-thinking investors willing to navigate the volatility.
Those able to adapt their strategies—through consolidation, domestic repositioning, or selective global engagement—could emerge stronger.
As healthcare innovation faces one of its most challenging environments, more difficult still than 2024, agility, foresight, and leadership will ultimately determine which Digital Health players thrive in this evolving landscape.