TL;DR
- Mental health investment in digital health surged to $2.7B in 2024 across 184 deals, marking a 38% year-on-year increase.
- Mental health now constitutes 12% of global digital health funding, reflecting strong investor confidence in the sector.
- AI-powered solutions saw a decline in mental health investment share, dropping from 53% to 48%.
- Late-stage funding reached its highest level since 2021, indicating a shift toward scaling proven mental health solutions.
- M&A activity remained strong, driven by venture-to-venture acquisitions of distressed startups.
- Corporate partnerships expanded in H1 2024, particularly among insurers and healthcare providers looking to integrate mental health in digital health solutions.
The Rise of Mental Health in Digital Health: Market Insights from 2024
In 2024, digital health experienced a resurgence, with global funding reaching $25.1 billion—a 5.5% year-over-year increase. A key driver of this growth was mental health investment, a sector that saw an impressive 38% rise in venture capital investment, solidifying its place as one of the most critical areas in digital health.
Why is Mental Health? The Catalysts Behind the Growth
Several converging factors are shaping the increasing demand for mental health solutions:
- A Global Mental Health Crisis: Rising cases of anxiety, depression, and burnout have placed significant strain on healthcare systems worldwide.
- Shift in Societal Perception: The stigma around mental health is diminishing, driving greater demand for accessible care solutions. Unlike previous generations, millennials are more open about mental health and actively seek support.
- Technological Advancements: AI-powered therapy tools, digital therapeutics, and remote mental health platforms are becoming mainstream, offering scalable and personalised care.
The Mental Health Investment Boom
After years of turbulence, mental health funding has re-emerged as a bright spot in digital health investment, rebounding sharply in 2024. The sector attracted $2.7 billion in venture capital, a 38% increase year-on-year, making it one of the fastest-growing segments in healthcare technology.
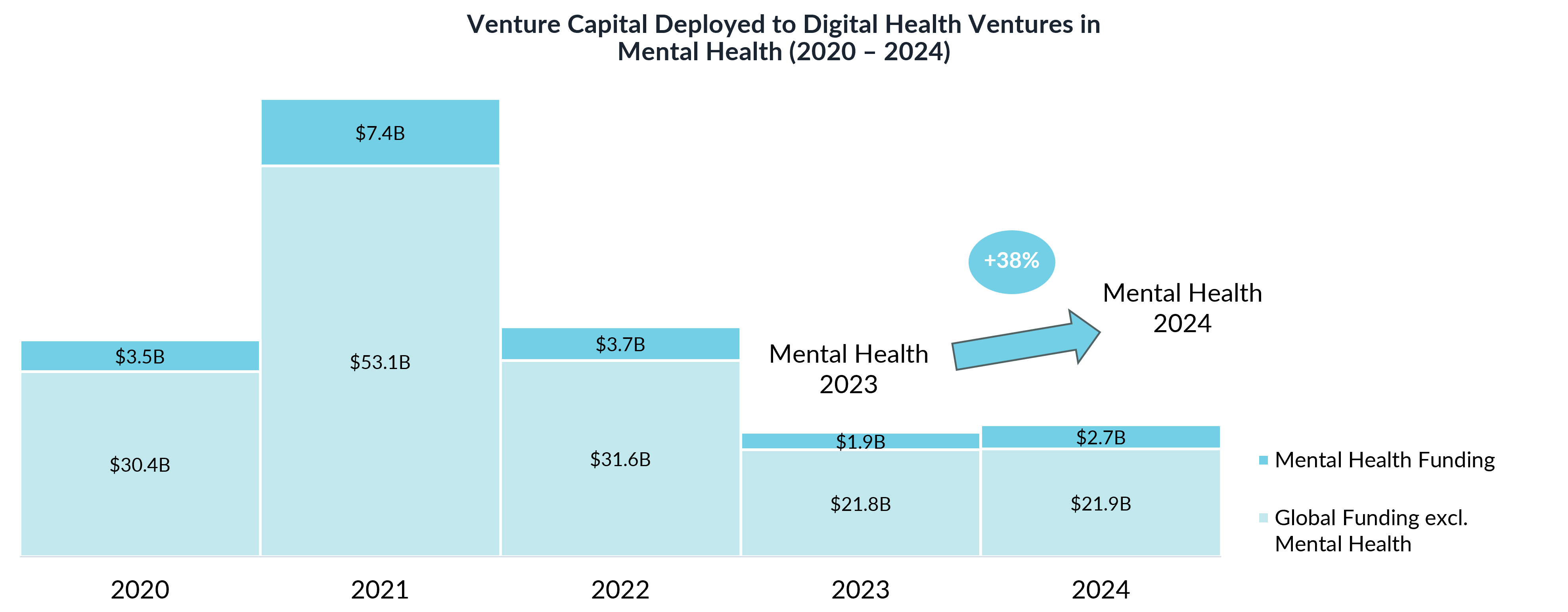
This growth is not merely a product of short-term investor sentiment. Societal attitudes toward mental health have shifted, with increasing corporate and governmental support for digital solutions. Meanwhile, the post-pandemic burnout crisis has driven employers and insurers to prioritise mental wellness offerings.
However, not all digital health segments experienced the same level of resurgence. Oncology remains the top-funded therapeutic category, but mental health is now in second place, overtaking neurology and cardiovascular diseases.
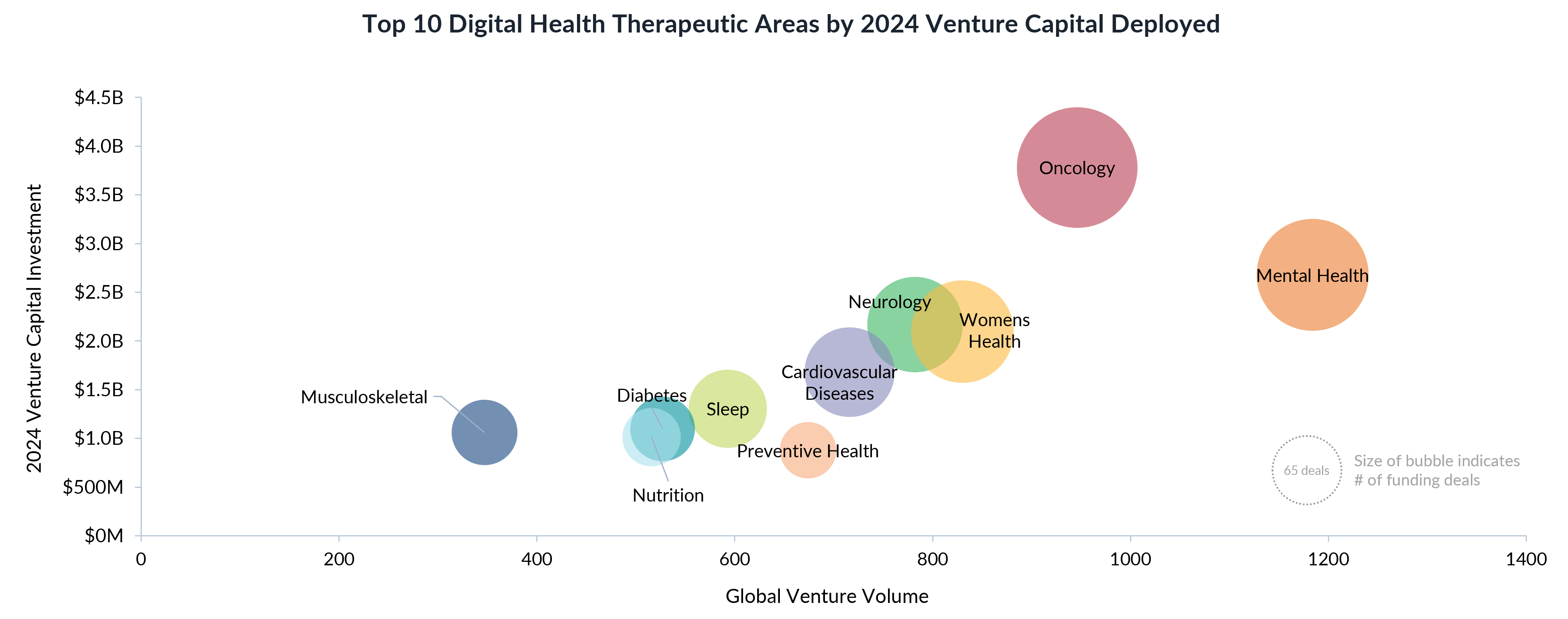
Investment Trends: Focus on Proven Solutions
Within mental health, investors have become more discerning, prioritising later-stage funding over early-stage bets. Series C and beyond rounds accounted for the highest funding levels since 2021, indicating strong interest in scaling companies with proven market traction.
Talkiatry stands as a notable player within this cluster, pioneering mental health care through virtual visits, allowing patients to receive care from their home. Notably, in June 2024, the company closed a Series C funding round of $130 million, further fueling its innovative initiatives.
This shift suggests investors are doubling down on mental health companies with established revenue streams rather than placing risky bets on unproven startups. Venture capital investors with the most mental health portfolio companies include General Catalyst, Lightspeed Venture Partners, and Khosla Ventures.
AI in Mental Health: A Declining Focus?
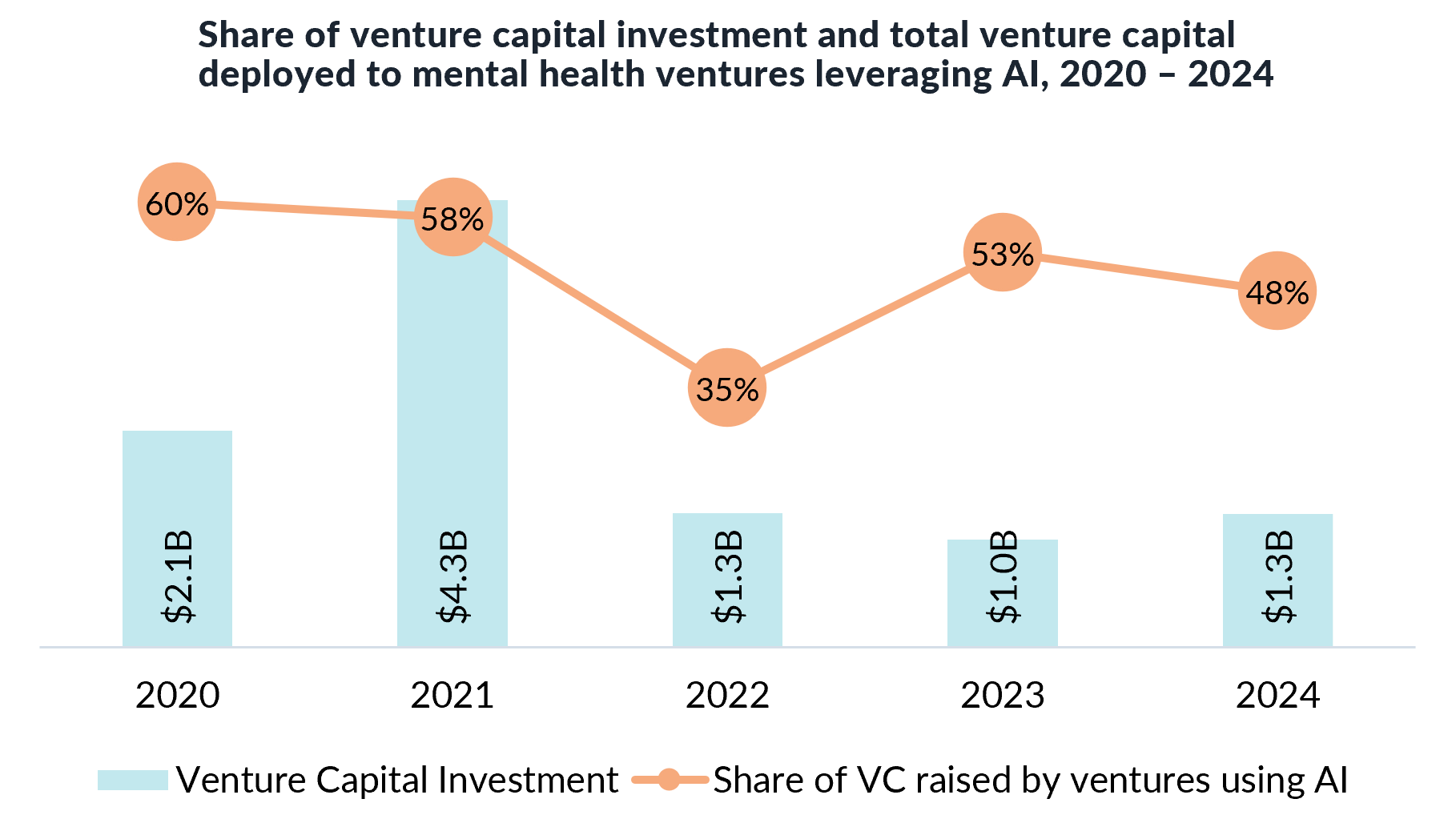
One of the most surprising findings in 2024 was the declining focus on ventures using AI in mental health investments. While AI-powered healthcare solutions have gained traction across diagnostics and drug discovery, its application in mental health is not driving investor enthusiasm.
- In 2023, 53% of mental health funding went to AI-driven ventures.
- In 2024, that number dropped to 48%.
This does not mean AI has no role in mental health; investors appear to be prioritising solutions with immediate clinical validation and regulatory approval over experimental AI-driven models. For example, in July 2024, Wisdo, a mental health app specialising in AI-assisted peer support groups, published a study showcasing the effectiveness of its solution. AI plays an increasingly important role in all aspects of digital health, including ventures in mental health. However, the 2024 surge in venture funding for mental health ventures was likely independent of investor interest in AI technology.
M&A and Partnerships: The Industry Consolidates
Acquisition Surge Fueled by Stressed Assets
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) within mental health remained strong, primarily driven by the sale of financially distressed startups.
- 71% of mental health M&A deals in 2024 were venture-to-venture transactions.
- Large digital health players acquired smaller startups to expand product portfolios and integrate AI-driven solutions.
Corporate Partnerships Expand, But Slow in H2
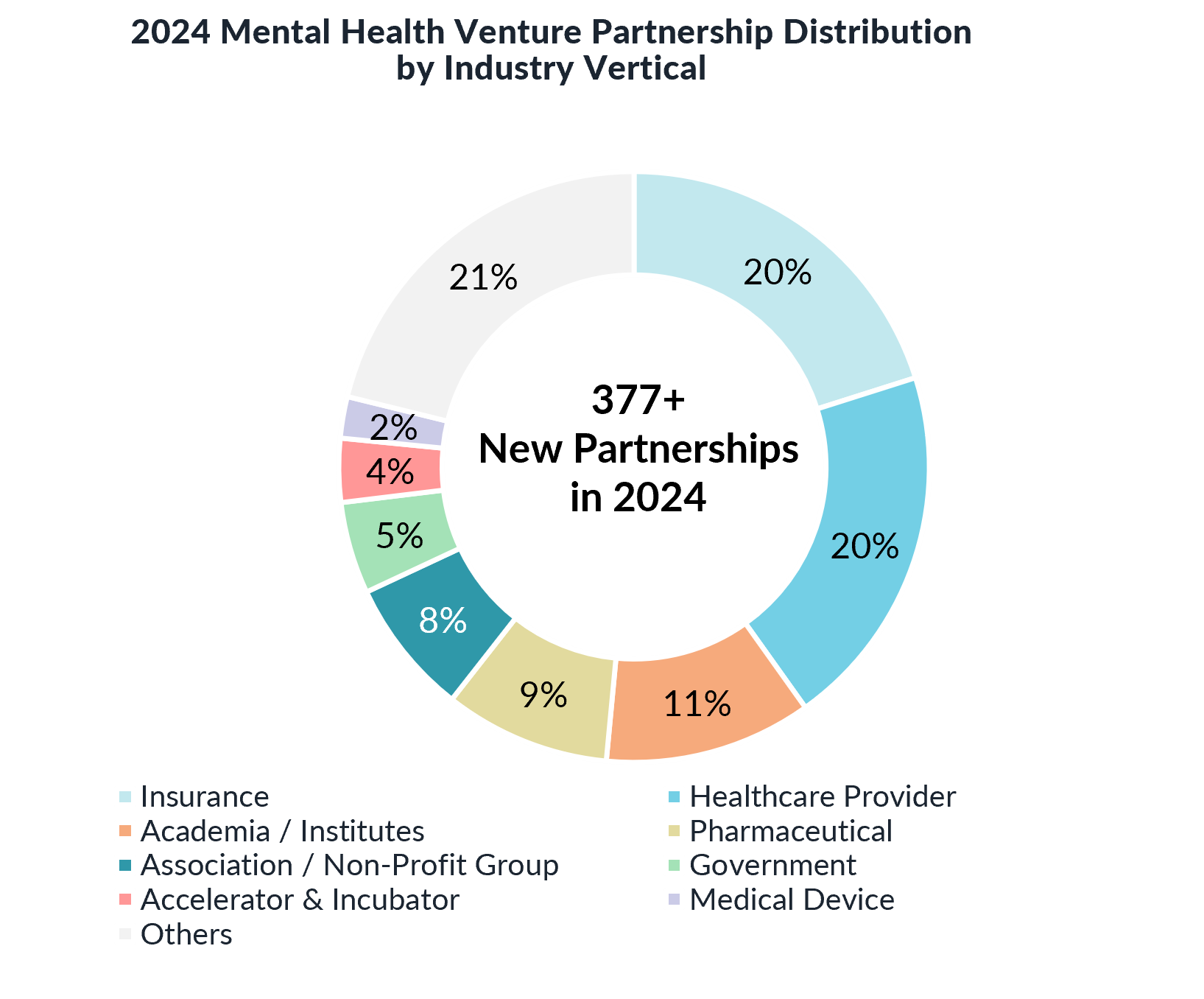
Partnerships between mental health startups and corporate players surged in H1 2024 but dropped by 29% in H2, reflecting broader market uncertainties.
Healthcare providers and insurers drove 40% of new partnership announcements in 2024 for mental health companies, integrating digital mental health tools into traditional care models.
- Virtual therapy and telepsychiatry solutions have become a focus for insurers looking to expand mental health coverage while controlling costs. In October 2024, MassMutual took bold steps by announcing that its policyholders could access Wysa, a mental health company offering an AI-enabled life coach for mental and emotional wellness.
- Integrating mental health tools into broader disease therapy has shown potential to improve patient adherence and overall therapy outcomes, reinforcing the need for seamless mental health support across all aspects of healthcare.
- Employers are increasingly incorporating digital mental health benefits into their corporate wellness programmes, responding to the growing demand for workplace mental health support.
This shift underscores a broader industry trend where digital solutions are no longer considered supplementary but essential components of comprehensive healthcare delivery.
Market Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite strong growth, the mental health in digital health sector faces obstacles:
- Scepticism around AI in therapy: Regulatory concerns and patient trust in AI-driven mental health interventions must be addressed.
- Clinical validation hurdles: In 2023, 38 digital mental health solutions received regulatory approval, but in 2024, that number dropped to 25, reflecting a 34% year-on-year decline.
- Slower adoption by healthcare systems: Integration with traditional healthcare models and reimbursement frameworks remains inconsistent.
However, mental health investment is expected to grow further as demand surges and digital health technologies mature.
Why This Matters for Investors, Startups, and Industry Leaders
For Investors:
The mental health market presents a high-growth opportunity, but success will depend on backing scalable, clinically validated solutions. The shift towards late-stage funding indicates a preference for startups with proven traction over speculative early-stage plays.
For Startups:
Regulatory compliance is becoming a significant barrier to entry. While funding is available, startups must prioritise evidence-based outcomes and regulatory approvals to remain competitive.
For Industry Leaders: With insurers and healthcare providers increasingly integrating mental health solutions, corporate partnerships represent a key growth channel. However, the slowdown in H2 partnership activity suggests that companies must adapt to market dynamics.
Methodology: Data Behind the Insights
The analysis in this report is based on proprietary data from HealthTech Alpha, Galen Growth’s leading digital healthcare technology intelligence platform. The platform tracks 750M+ data points and 14,800+ ventures globally.
The report focuses on mental health ventures that:
- Were incorporated after 2002.
- Meet Galen Growth’s Digital Health taxonomy.
- Are not subsidiaries of large corporations.
- Have secured venture funding up to pre-exit stages.








