Why is generative AI becoming central to healthcare and pharma?
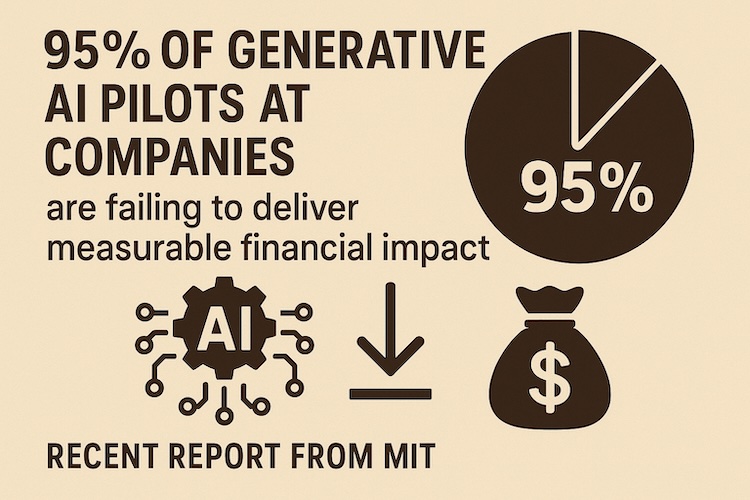
A recent report from MIT’s NANDA initiative reveals a sobering reality: 95% of generative AI pilots at companies are failing to deliver measurable financial impact. Based on 52 interviews with enterprise stakeholders, surveys of 153 industry leaders, and analysis of more than 300 public AI deployments, the study found that only 5% of pilot programmes achieve rapid revenue acceleration.
This matters for healthcare and pharmaceuticals, where expectations of AI are exceptionally high. While generative AI holds extraordinary promise, most corporate initiatives are stalling. The MIT study pinpoints the reasons:
- The “learning gap” – the main issue is not weak AI models but poor integration. Companies don’t know how to embed generative AI into workflows. Generic tools such as ChatGPT, while flexible for individual use, often fail in enterprise contexts.
- Misguided investment – more than half of corporate AI budgets are directed towards sales and marketing, even though the highest returns come from back-office automation.
- Partnership advantage – companies that purchase AI tools from specialised vendors achieve a 67% success rate, far higher than those developing solutions in-house.
The message is clear: the winners in generative AI will not be those who dabble in pilots, but those who learn, partner, and scale responsibly.
How is pharma moving beyond pilots?
Despite the failings highlighted by MIT, the pharmaceutical sector shows how generative AI can succeed when applied with focus and expertise.
The Galen Growth Pharma Innovation Report 2024 demonstrates that since 2020, 72% of digital health ventures partnering with pharma have leveraged AI or generative AI . Unlike many industries stuck in pilot mode, pharma is embedding AI directly into core operations.
Key use cases include:
- Drug discovery – generative AI accelerates the design of novel molecules and targets.
- Clinical trials – AI tools improve patient recruitment, simulate outcomes, and enable real-time monitoring.
- Patient engagement – platforms such as LillyDirect and PfizerForAll integrate AI into telehealth, adherence tools, and digital pharmacies.
These successes align directly with MIT’s conclusion: companies that partner with specialised vendors, rather than relying on generic tools, dramatically improve success rates.
Why is investment in AI healthcare ventures rising?
The market is voting with its wallet. In H1 2025, AI-enabled ventures captured 65% of all digital health funding, raising $7.8 billion.
This reflects two trends:
- Investors are backing proven use cases – capital is flowing to ventures that demonstrate measurable outcomes.
- Pharma’s adoption de-risks innovation – partnerships with large corporates validate startup technology and accelerate scaling.
By contrast, industries that rely on generic tools without domain expertise see stalled adoption and wasted budgets.
What makes generative AI different in healthcare?
Generative AI goes beyond analysing patterns—it creates new possibilities.
- Drug discovery: simulating molecules and generating new candidates.
- Clinical trials: modelling trial scenarios, improving recruitment, and reducing attrition.
- Patient support: personalised interactions, reminders, and behavioural monitoring.
The MIT findings reinforce that context matters. Generic GenAI tools may generate output, but only domain-specific applications, embedded into workflows, deliver financial and clinical impact.
Why relying on generic GenAI search engines is risky
A growing number of corporate decision-makers, particularly middle management, are deferring or terminating contracts with research providers, under the belief that generative AI search engines will replace them. The MIT NANDA report proves this to be a false economy: 95% of pilots fail because generic tools cannot adapt to complex workflows or regulated environments.
For healthcare, the risks are even greater: generic models often produce incomplete, misleading, or non-evidence-based outputs that cannot withstand regulatory or clinical scrutiny.
How Galen Growth and HealthTech Alpha bridge the gap
Working with Galen Growth and HealthTech Alpha addresses precisely the failures that MIT identified:
- Domain-specific intelligence – HealthTech Alpha is built on the world’s most comprehensive digital health dataset, curated and clinically validated.
- Evidence-based insights – 70% of pharma’s AI partnerships involve ventures with proven clinical strength. Our platform highlights these proof points, ensuring decisions are grounded in reality.
- Workflow integration – Alpha Copilot, our GenAI-powered research assistant, is designed to integrate into enterprise workflows, delivering trusted answers with transparent sourcing.
- Specialist partnership advantage – MIT’s research shows specialised vendors deliver a 67% success rate versus much lower rates for in-house or generic builds. Galen Growth is exactly that specialist partner.
In short, replacing market research with generic AI search leads to failure. Partnering with Galen Growth maximises success.
Lessons for healthcare and beyond
Pharma’s adoption of AI offers three critical lessons:
- Move quickly beyond pilots – pilot purgatory kills momentum.
- Anchor in clinical evidence – ventures that prove outcomes will win partnerships.
- Partner with specialists – as MIT confirms, partnerships outperform in-house or generic deployments.
Opinion: The road ahead
Taken together, the MIT NANDA report and Galen Growth’s data show both the risks and opportunities of generative AI. The risk is obvious: most initiatives fail due to lack of strategy, poor investment focus, and reliance on generic tools. The opportunity is equally clear: when applied with focus, evidence, and partnerships, generative AI transforms pharma and healthcare.
Our view: generative AI is becoming the cornerstone of healthcare innovation. The winners will not be those who cut costs by cancelling research contracts in favour of generic AI, but those who partner with domain specialists, validate outcomes, and scale responsibly.